Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
2 School of Computer Science, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan 430068, China
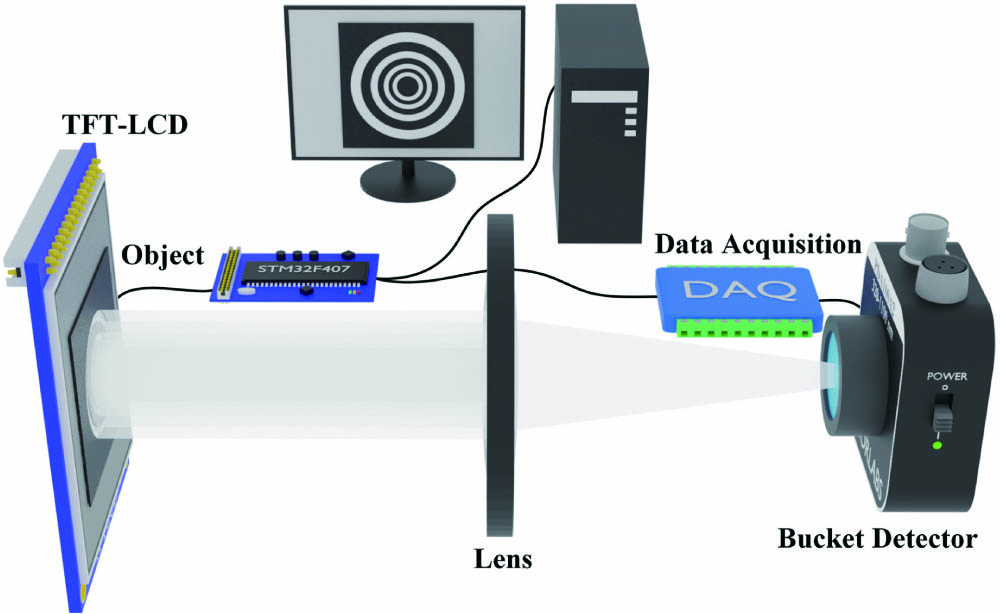
The array spatial light field is an effective means for improving imaging speed in single-pixel imaging. However, distinguishing the intensity values of each sub-light field in the array spatial light field requires the help of the array detector or the time-consuming deep-learning algorithm. Aiming at this problem, we propose measurable speckle gradation Hadamard single-pixel imaging (MSG-HSI), which makes most of the refresh mechanism of the device generate the Hadamard speckle patterns and the high sampling rate of the bucket detector and is capable of measuring the light intensity fluctuation of the array spatial light field only by a simple bucket detector. The numerical and experimental results indicate that data acquisition in MSG-HSI is 4 times faster than in traditional Hadamard single-pixel imaging. Moreover, imaging quality in MSG-HSI can be further improved by image stitching technology. Our approach may open a new perspective for single-pixel imaging to improve imaging speed.
single-pixel imaging array spatial light field measurable speckle gradation Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031104
红外与激光工程
2021, 50(12): 20210657
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
Typical single-pixel imaging techniques for edge detection are mostly based on first-order differential edge detection operators. In this paper, we present a novel edge detection scheme combining Fourier single-pixel imaging with a second-order Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) operator. This method utilizes the convolution results of an LoG operator and Fourier basis patterns as the modulated patterns to extract the edge detail of an unknown object without imaging it. The simulation and experimental results demonstrate that our scheme can ensure finer edge detail, especially under a noisy environment, and save half the processing time when compared with a traditional first-order Sobel operator.
single-pixel imaging edge detection Laplacian of Gaussian operator Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(12): 121101
湖南大学信息科学与工程学院, 湖南 长沙 410082
风导致的信道气流是影响关联成像的重要因素,因此,对信道气流干扰下的关联成像研究进行了总结。首先,给出了近场气流影响的相位模型,并从光传输和关联成像两个角度进行了可靠性验证;然后,将该模型扩展到高风速区域,得到超声速气流下风速和边界层厚度对关联成像的影响规律,定量分析了成像质量的变化情况;最后,针对实际成像过程中的探测抖动问题,介绍了基于关联成像时间特性的抑制方法以及小样本成像算法。本研究结果不仅可以评估信道气流对关联成像的影响,还为关联成像在机载遥感等领域的应用提供了重要的参考价值。
量子光学 量子信息与处理 湍流 图像恢复技术 近场气流 关联成像 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(10): 1011017
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
The scattering medium is usually thought to have a negative effect on the imaging process. In this paper, it is shown that the imaging quality of reflective ghost imaging (GI) in the scattering medium can be improved effectively when the binary method is used. By the experimental and the numerical results, it is proved that the existence of the scattering medium is just the cause of this phenomenon, i.e., the scattering medium has a positive effect on the imaging quality of reflective GI. During this process, the effect from the scattering medium behaves as the random noise which makes the imaging quality of binary ghost imaging have an obvious improvement.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(12): 12001468
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China
We present an experimental demonstration of ghost imaging of reflective objects with different surface roughness. The influence of the surface roughness, the transverse size of the test detector, and the reflective angle on the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is analyzed by measuring the second-order correlation of the light field based on classical statistical optics. It is shown that the SNR decreases with an increment of the surface roughness and the detector’s transverse size or a decrease of the reflective angle. Additionally, the comparative studies between the rough object and the smooth one under the same conditions are also discussed.
Image processing Coherence imaging Statistical optics Roughness Photonics Research
2017, 5(4): 04000372





